Climate Alarmism
The oldest trick in the book.
What is air temperature?
You can measure temperature with a thermometer. It gives a value on a linear temperature scale, but the physics
behind it are not linear at all. If you try to correlate it with the radiation balance of earth it gets even less linear.
Our temperature scales are based on the kinetic theory approach to temperature. (classical mechanics)
Temperature is the average kinetic energy of molecules in the form of translations, vibration and rotation. The mass
and degrees of freedom of molecules are different for every molecule. So, every molecule has its own unique constant
for how much energy is needed to increase these translational, vibrational and rotational effects.
The constants are usually expressed in ΔK/g instead of ΔK /molecule. In our macroscopic world measuring mass is much
easier than the number of molecules.
To get an exact average ΔK/g for a mixture of molecules you have to add the mass fraction of each molecule together.
(not the volume fraction. )
Example dry air:
78%: Nitrogen (1.04 J/gK)
20: Oxygen (0.918 J/gK)
1%: Argon (0.52 J/gK)
Air (1.0035)
Fairly simple so far, but on Earth dry air doesn’t exist naturally. It is always mixed with water vapour.
The amount of vapour is never constant. Water constantly evaporates from bodies of water, soil and plants.
It rises through the air column; the wind moves it around and eventually it condenses into clouds and falls
out as rain or snow. You may have seen the term humidity in weather forecasts. This a fraction of how
saturated the air is with water vapour. At 100% the air cannot take up any more water vapour. Any additional
water condenses into droplets and form clouds or fog which is just a cloud at ground level. During condensation
the energy that was required to make water vapour gets released again.
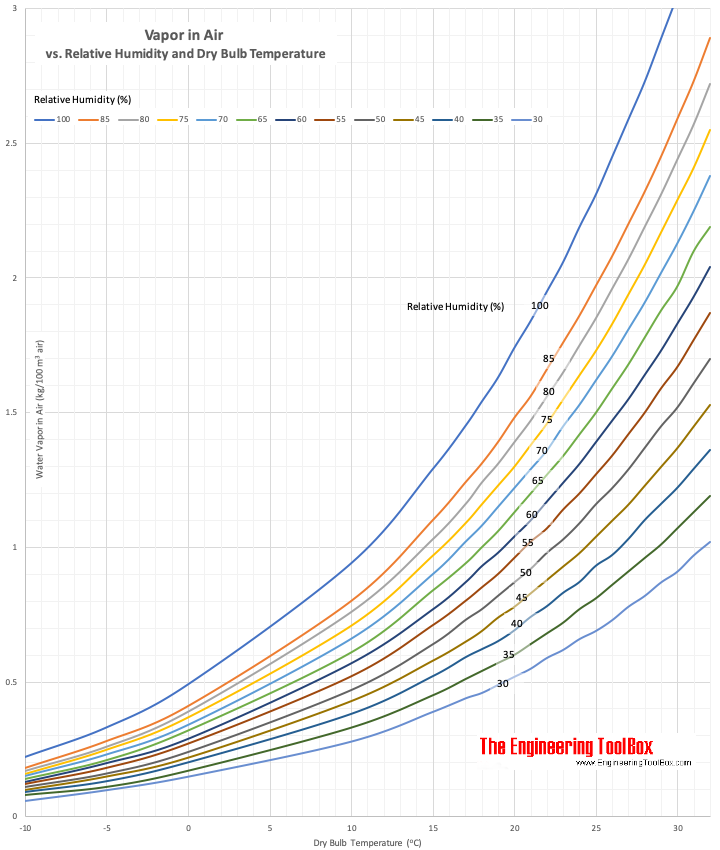
Figure 1: Saturation curves for air. (https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/steam-humid-air-d_260.html)
Due to the non-linear saturation curve 50% humidity at 10C holds less water vapour than 50% humidity at 20C.
At ~2% mass fraction water vapour doesn’t change the heat capacity of air significantly. Wet air with 2%
vapour has a heat capacity of 1.037J/gK. (a 3.71% increase)
Far more impactful are the phase changes of water (melting and evaporation)
Energy of the water cycle:
ice at -10C: 2J/gK
water at 25C: 4.14 J/gK
vapour at 25C: 1.864 J/gK
heat of fusion: melting: 333J/g (melting)
heat of vaporization: 2270 J/g (evaporation)
It takes 2270J/g to turn water into vapour. It’s the same energy as heating the same mass of air from 0C to 2262C.
Or using the 2% mass fraction to 45C. (2263 * 0.02) For melting ice the values are 331C and 6.63C respectively.
Note: This temperature increase can only happen by an instant power burst, like an explosion.
At natural power levels like sunshine the black body radiation limits the maximum temperature.
From these values we can conclude that in places where water can evaporate or melt, the heat capacity of dry air
doesn’t matter at all. We only measure the water cycle.
And it just so happens that humans systematically limited the water cycle on millions of square kilometres of land.
The main causes are deforestation, land drainage for agriculture and infrastructure. It can be directly measured
and visualized with satellites. A simple temperature graph from a thermometer doesn’t tell you if a hot value was
caused by the weather, a new nearby parking lot absorbing all incoming solar energy or a tall new housing complex
blocking cool, humid winds from the ocean.
Due to this land change hot summers will stay with us forever, even if CO2 drops to zero ppm.
It possibly gets even hotter in summer during the day. Colder oceans mean less water evaporates
and makes it on land, overall making it dryer. Then you get more natural deserts and more extreme
temperature changes. Winter will get colder as well as there is less water to freeze. (e.g., The moon
with zero atmosphere or water has temperature range from -170C to +120C at the equator from a day night
cycle lasting 29.5 days)
The Ross Ice shelf in Antarctica is almost at sea level (full atmosphere to retain heat including CO2), near zero water vapour
and easily reaches -60C during winter.
In most places during the last ice ages the climate was dryer than it is today.
Black Body Radiation
Earth can only loose heat to space through radiation. Space is mostly empty and won’t conduct any heat away. The amount of energy radiated away is dependent on the temperature to the power of four. This is not a linear increase. Any additional degree will radiate more energy away then the previous one and be harder to maintain.
In order to raise the temperature from -30C to -25C you need 17W per square meter.
To raise it from 25C to 30C you need 31W per square meter.
This is one of the reasons why most warming will happen in the polar regions. The tropics are already warm
and keeping them even warmer is much more difficult.
These values aren’t the real heat loss of Earth. A clear atmosphere retains around 35% of this outgoing radiation
from the surface. Local variations occur due to varying water vapour, by far the most potent greenhouse gas.
Thick clouds can retain all outgoing radiation from the surface and only release their own radiation to space.